Authors: Ivan Fistonic and Nikola Fistonic
Published in: Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. 2018;50(1):1-7
1. NEW PREDICTIVE MODEL FOR ASSESSING EXPECTED RESULTS OF SUI LASER TREATMENT
Dr. Ivan Fistonic et al. developed a new predictive model which will help practitioners assess the expected result of SUI laser treatment. The model identifies four key pre-intervention predictors which effect short-term Er:YAG outcomes.
2. METHOD
An analysis was performed on a sample of 84 female patients ranging in age from 30 to 70 who suffered from SUI. The patients were treated with a 2940 nm wavelength Er:YAG Fotona laser. In a three-step protocol (30 days in between), the laser irradiation was applied to the anterior vaginal wall, the entire circumference of the vaginal canal, and the vestibule area. The analyzed predictors were: patient age; body mass index; number of births; average birth weight; last delivery weight; menopausal status; pelvic floor muscle strength (PFMS) of the pelvic diaphragm; adequacy of anatomic support to the bladder neck and urethro-vesical angle measured by Q-tip elevation; ICIQ-UI baseline, pre-intervention value.
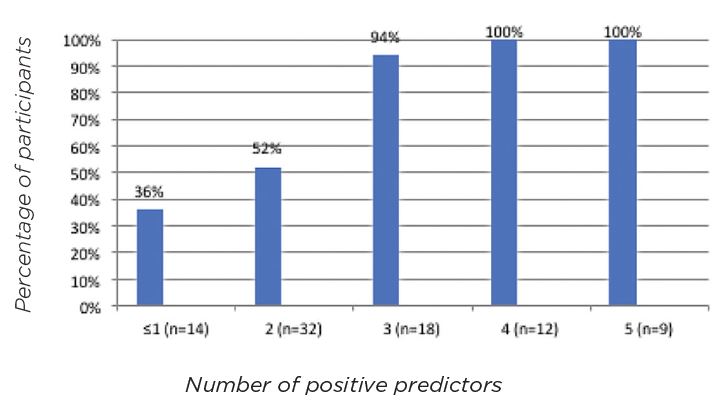
3. RESULTS IDENTIFY FOUR KEY PREDICTORS EFFECTING OUTCOME
The study reveals that age, body mass index, Q-tip elevation, and ICIQ-UI values prior to treatment are the four predictors that can be used to assess the outcome of laser treatment for SUI in female patients. The effects of laser treatment were evident by an absolute change in the ICIQ-UI SF score and a relative decrease of 30% in the ICIQ-UI score 2–6 months after the treatment. The association between the Q-tip test and treatment outcomes was moderated by age. Q-tip was a significant predictor for patients between 44 and 53 years of age.